Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in the cells of your body and in the foods you eat. While it is essential for various bodily functions, having high levels of cholesterol can lead to serious health problems, particularly cardiovascular diseases. This patient leaflet aims to educate you about high cholesterol, its risks, and practical steps you can take to correct it and maintain a healthier heart.
Understanding High Cholesterol:
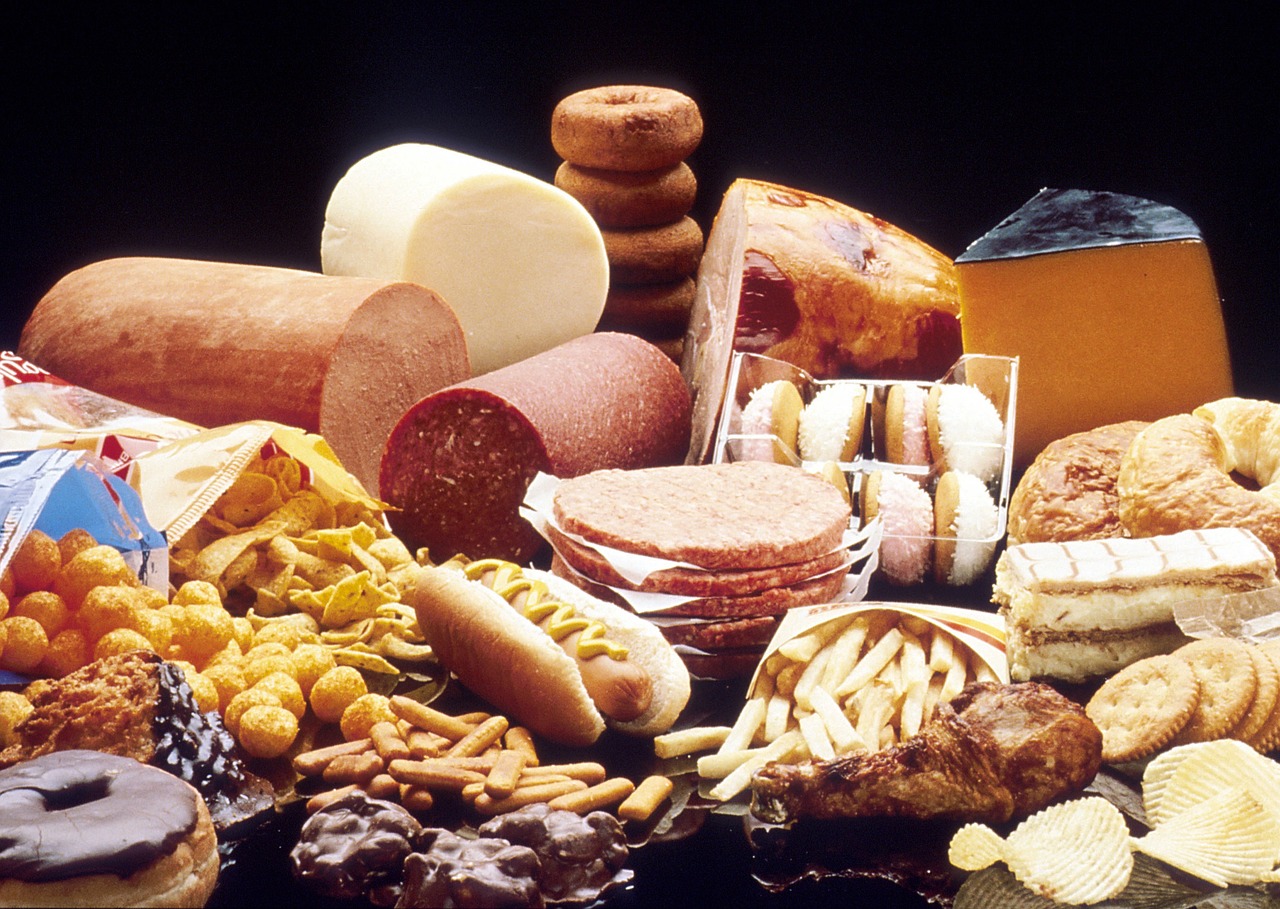
High cholesterol, also known as hypercholesterolemia, occurs when there is an excessive amount of cholesterol in your blood. The two main types of cholesterol are low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, as it can build up on the walls of your arteries and form plaque, leading to a condition called atherosclerosis. HDL, on the other hand, is known as “good” cholesterol, as it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the arteries.
Risks of High Cholesterol:
Having high cholesterol can increase your risk of developing various cardiovascular conditions, including:
1. Coronary artery disease (CAD): Plaque buildup in the arteries can restrict blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain (angina) or even a heart attack.
2. Stroke: Plaque can also block blood flow to the brain, leading to a stroke.
3. Peripheral artery disease (PAD): Narrowed arteries in the legs can cause pain and limited mobility.
4. Atherosclerosis: Chronic plaque buildup can weaken the arterial walls and lead to an aneurysm.
Lifestyle Changes for Correcting High Cholesterol:
Fortunately, high cholesterol can often be managed through lifestyle changes. Before starting any new regimen, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice. Here are some general guidelines to help correct high cholesterol:
1. Heart-Healthy Diet:
– Reduce saturated fats: Limit foods high in saturated fats, such as red meat, full-fat dairy products, and tropical oils like coconut and palm oil.
– Increase fiber intake: Consume more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to improve cholesterol levels.
– Include heart-healthy fats: Consume sources of unsaturated fats, like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
– Omega-3 fatty acids: Incorporate fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel) into your diet or consider omega-3 supplements with your doctor’s approval.
2. Regular Physical Activity:
– Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
– Include activities like brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing.
– Exercise helps raise HDL cholesterol and improve overall cardiovascular health.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
– If overweight, losing just 5-10% of your body weight can significantly improve cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
4. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol:
– Smoking damages blood vessels and lowers HDL cholesterol. Quitting smoking offers significant cardiovascular benefits.
– If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation. For men, this means up to two drinks per day, and for women, up to one drink per day.
5. Manage Stress:
– Chronic stress can impact cholesterol levels. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or hobbies you enjoy.
6. Regular Health Check-ups:
– Visit your healthcare provider regularly for cholesterol screenings and overall health assessments.
Medical Treatment for High Cholesterol:
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to correct high cholesterol. Your healthcare provider may recommend medication to help manage your cholesterol levels effectively. Common medications include:
– Statins: These drugs lower LDL cholesterol and may slightly increase HDL cholesterol.
– Bile acid sequestrants: They bind to bile acids in the intestine, reducing cholesterol absorption.
– Ezetimibe: This medication blocks cholesterol absorption in the small intestine.
Conclusion:
Correcting high cholesterol is crucial for a healthier heart and overall well-being. By making positive lifestyle changes and, if necessary, following medical treatment, you can reduce your risk of developing serious cardiovascular conditions. Remember to consult your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet or exercise routine. Empower yourself with knowledge and take proactive steps to achieve optimal heart health for a happier and longer life.